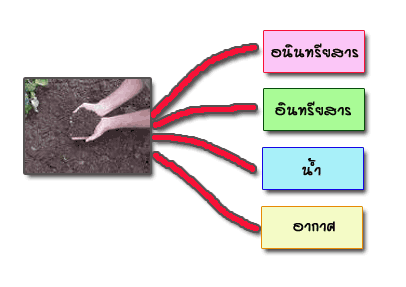
Soil composition
Objects or inorganic minerals are most abundant in the common ground. Derived from the weathering of rocks and mineral dissolution. Inorganic objects In the soil in parts of the soil particles, which have many different shapes and sizes to be divided into 3 groups. 1. sand particles (2.00 to 0.05 mm in diameter) 2. silt particles (Diameter 0.05 to 0.002 mm) 3. clay (Diameter <0.002 mm.) And. Objects or inorganic minerals in soil. Is important in controlling the nature of the soil. A source of plant nutrients. And a source of food for soil microorganisms. In addition, the particle size of the clay is the most important part of the chemical processes in the soil. Soil organic matter This covers a significant part of the fossil is degraded. microorganisms Both the living and the dead. The decomposition of organic matter. Or being synthesize new ones. It does not include plant roots Or language processing plant Or animals that are not biodegradable. Organic matter in the soil An important source of plant nutrients. And as a source of food and energy for soil microbes, especially nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur are the most important influence on the properties. Soil physical, chemical and biological properties such as soil structure, porosity, drainage and aeration. To absorb water and nutrients in the soil. Which continue to affect the fertility of the soil. And the ability to provide products of the soil. |
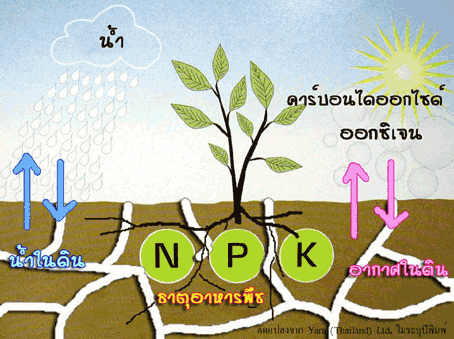
Soil water refers to the water that is found in the spaces between soil particles or soil. Is very important to plant. And plant growth As an aid in dissolving nutrients in the soil and is an important part of moving nutrients from the roots to all parts of the plant.
Means of various gases Inserted in the spaces between soil particles in the water is. The gas is typically found in soil nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2), which plant roots and soil microbes used in breathing. And energy in existence.

ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น